📚 Index
-
What You'll Learn
-
What Is a 1031 Exchange?
-
Why Use a 1031 Exchange: Key Benefits
-
IRS Rules & Requirements
-
Types of 1031 Exchanges
-
Step‑by‑Step Process
-
Real-Life Examples
-
Statistics You Should Know
-
Practical Tips for Success
-
Summary Table
-
Conclusion
-
FAQs
1. What You’ll Learn
-
The fundamentals of 1031 exchanges
-
How these transactions help defer capital gains taxes
-
Important IRS timelines and rules
-
Different types of exchanges
-
Practical, real-life scenarios
-
Eye-opening statistics and useful tips
2. What Is a 1031 Exchange?
A 1031 exchange—named after Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code—is a tax strategy that allows investors to defer capital gains taxes by swapping one investment property for a like-kind one
What makes it unique:
-
Applicable only to real estate (since 2018)
-
Must involve business or investment property, not personal residences
-
Utilizes a Qualified Intermediary (QI) to ensure you never receive sale proceeds directly
3. Why Use a 1031 Exchange: Key Benefits
-
Tax Deferral
Avoid paying up to 25–30% in capital gains taxes by rolling proceeds into a new property -
Compound Wealth
Instead of losing money to taxes, investors reinvest full proceeds—accelerating portfolio growth . -
Flexibility
Change property types, expand your holdings, or move to different locations—all while deferring taxes -
Economic Boost
Roughly 10‑20% of commercial real estate transactions use 1031 exchanges, supporting half a million jobs and generating over $7 billion in tax revenue
4. IRS Rules & Requirements
-
Like‑Kind: Both properties must be similar in nature—both real estate
-
Investment Use: Property must be held for business or investment—not for personal residential use
-
Timeline:
-
Identify replacement property in 45 days
-
Close the deal within 180 days
-
-
Qualified Intermediary: Must be used to hold proceeds and avoid direct receipt .
-
Boot Rules: Any non-like-kind proceeds ("boot") are taxable
5. Types of 1031 Exchanges
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Simultaneous | Sell one property and buy another immediately. Complex to coordinate |
| Deferred (Delayed) | Most common: Sell first, identify and close on replacement within time limits . |
| Reverse Exchange | Buy first, then sell your old property—still need QI and same deadlines . |
| Construction/Improvement Exchange | Use exchange funds to improve replacement property during the 180-day window. |
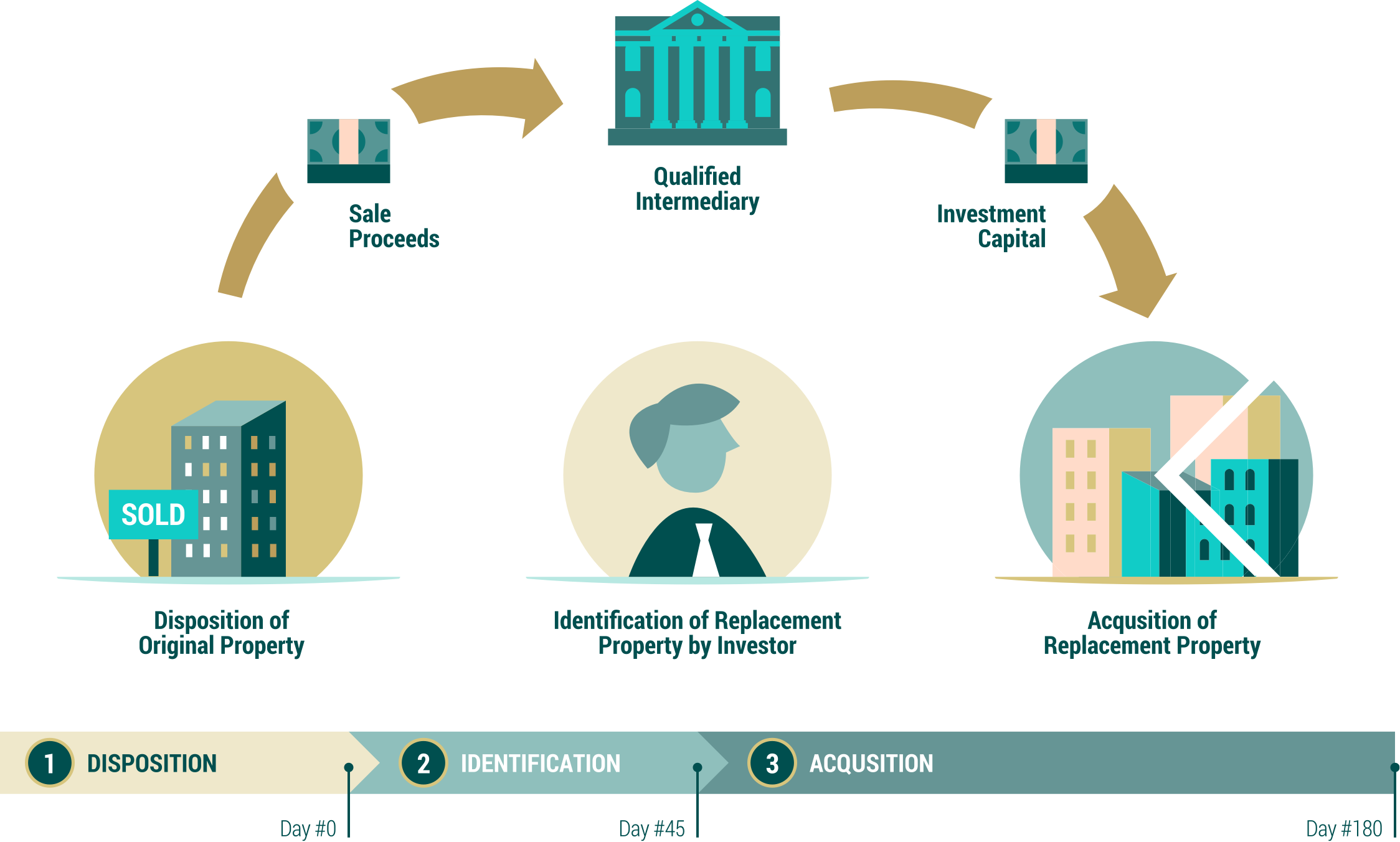
6. Step‑by‑Step Process
-
Hire a Qualified Intermediary
-
Sell Your Relinquished Property
-
45‑Day Identification: In writing and delivered to your QI
-
Close Within 180 Days
-
File IRS Form 8824 on your tax return
7. Real-Life Examples
Example 1: Small Investor
Raja sells a ₹1.0 crore rental home (₹30 lakh gain). Instead of paying ₹7.5 lakh in capital gains tax, he uses a 1031 exchange to buy a ₹1.05 crore commercial unit. He rolls the full proceeds into the new purchase.
Example 2: Portfolio Upgrade
Sneha swaps three small rental apartments worth ₹2.5 crore for a ₹3.0 crore multi-family complex. She defers ~₹50 lakh in taxes and secures stable income from a higher-end property.
8. Statistics You Should Know
-
10–20% of commercial RE deals use 1031 exchanges
-
Supports 568,000 jobs and generates $7.8B in government revenue annually
-
Majority of deals involve properties under $1M
9. Practical Tips for Success
-
✔️ Plan ahead. Holiday or financing delays can cause missed deadlines .
-
✔️ Work closely with experts. Real estate agents, tax pros, QI.
-
✔️ Understand 'boot'. Even small cash take‑outs can trigger tax liability .
-
✔️ Track documentation. Keep all records—identification notices, QI agreements, deeds, Form 8824.
-
✔️ Stay flexible with properties. Use 3‑property or 200% rules or satisfy the 95% rule
10. Summary Table
| Feature | Rule/Benefit |
|---|---|
| Qualified Properties | U.S. real estate held for investment |
| Tax Deferral | Up to ~25–30% capital gains rate |
| Requirement | 45‑day ID + 180‑day close |
| Intermediary Needed | Yes — to avoid constructive receipt |
| Boot Taxable | Yes, if cash is taken out |
| Repeatable | Yes—multiple deferrals possible |
| Final Tax Trigger | Upon cash-out or inheritance |
| Estate Planning | Basis steps-up—tax burden removed |
11. Conclusion
A 1031 exchange is a powerful tool to defer taxes, build wealth, and optimize your real estate portfolio. With clear rules, strict timelines, and expert guidance, it offers flexibility and power to investors of all sizes. If used correctly and repeatedly, it can lead to nearly indefinite tax deferral—and a lasting legacy through estate planning.
12. Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Can my primary home qualify?
No—only investment or business-use properties. Personal residences aren't eligible
Q2: Can I tap exchange funds for improvements?
Yes—if done within 180 days and coordinated by your QI under a construction exchange.
Q3: What if I identify more than one property?
You can use the 3-property or 200% rule, or meet the 95% rule
Q4: What's a reverse exchange?
You can acquire new property before selling the old one—very complex but possible
Q5: Is 1031 indefinite?
Yes, until you cash out. At death, beneficiaries get a stepped-up basis—removing the deferred gain .
✅ Ready to Grow Your Investment Portfolio?
Take the next step confidently—with Manika FinTax Solutions. Our expert team handles end-to-end 1031 exchange filings, ensuring every IRS rule is met so you defer taxes properly and maximize your investment potential.
Contact us today to get personalized guidance and professional support. Your future self will thank you!
Keywords: 1031 exchange, defer capital gains tax, like-kind exchange, real estate investment, Qualified Intermediary, boot rules, delayed exchange, investment property swap, 45-day identification, 180-day rule.


Post a Comment
0Comments