🧭 Index: What You’ll Learn in This Article
-
Introduction – Why Form 1040 is essential
-
What Is Form 1040? – Purpose and who must file
-
Core Sections of Form 1040
-
Personal Information
-
Income Reporting
-
Adjustments & Deductions
-
Tax Calculation
-
Credits & Payments
-
Refund or Amount Owed
-
-
Supporting Schedules – When and why they matter
-
Key Stats & Trends – IRS data for added insight
-
Two Real-Life Examples – Walkthroughs to illustrate filing
-
Practical Tips – Avoid mistakes & maximize savings
-
Conclusion – Recap and next steps
-
FAQs – Boost SEO & clarity
-
Call to Action – Need help? Contact Manika Fintax Solutions
1. Introduction
If you’re a U.S. taxpayer, chances are you’ve heard of Form 1040. This fundamental IRS form guides Americans through claiming income, deductions, credits, and calculating their tax liability or refund. For many, it seems daunting—but don’t worry! At Learn with Manika, we break it down in simple, beginner-friendly terms. This guide empowers you to confidently file your taxes and decide when to seek pro assistance.
2. What Is Form 1040?
Form 1040, officially called “U.S. Individual Income Tax Return,” is the standard form used by individual taxpayers to report their income to the IRS
Who Needs to File?
-
U.S. citizens or residents with income above a certain threshold (e.g., $14,600 for single in 2024)
-
Anyone with special tax situations—like self-employment income over $400, alternative minimum tax, or HSA distributions—must file, regardless of income
3. Core Sections of Form 1040
Form 1040 is organized like a “building block” – you complete the main form and attach only the schedules relevant to your situation
A. Personal Information
-
Basic details: name, address, filing status, SSN, dependents
-
Ensure accuracy – errors here can delay your return or refund
B. Income Reporting
Report all income types: wages, interest, dividends, capital gains, retirement distributions, unemployment, etc.
C. Adjustments & Deductions
-
Standard Deduction – A fixed deduction based on filing status; e.g., $14,600 for single filers in 2024
-
Above-the-line adjustments – Subtractible before deductions (e.g., student loan interest, retirement contributions)
D. Tax Calculation
-
Use tax tables (based on taxable income) to find your tax
-
Add additional taxes like self-employment or AMT if applicable
E. Credits & Payments
-
Tax credits reduce what you owe dollar-for-dollar (e.g., child tax credit, education credit)
-
Payments already made via withholding or estimated taxes are entered here
F. Refund or Amount Owed
-
If your total payments exceed your tax, you get a refund
-
Otherwise, you owe the difference—remember, paying late can trigger penalties irs.gov
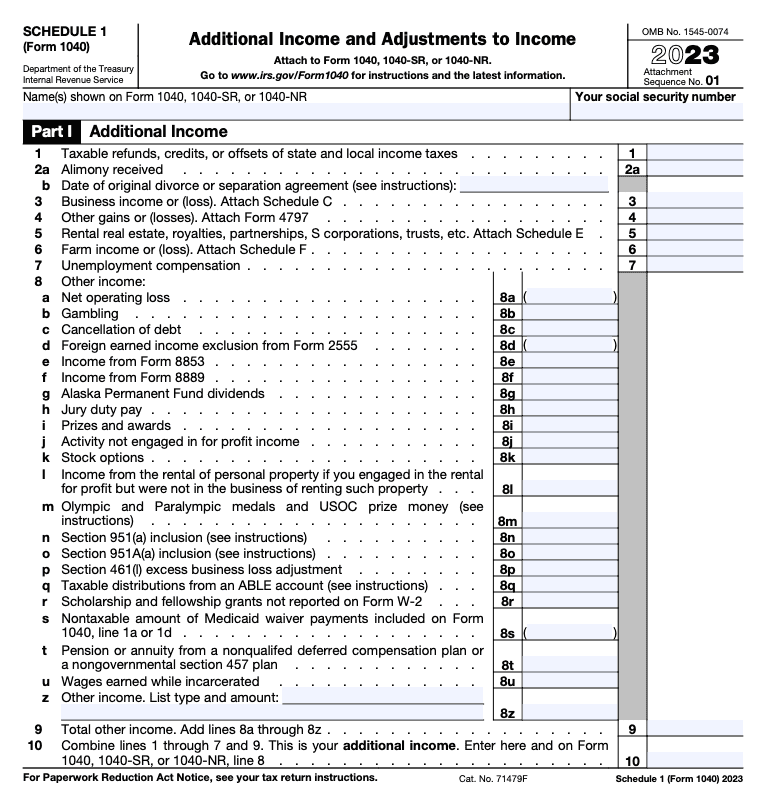
4. Supporting Schedules: When Do You Need Them?
| Schedule | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Schedule 1 | Income not covered on main form (e.g., business, rental, unemployment) |
| Schedule 2 | Additional taxes (e.g., self-employment tax, AMT) |
| Schedule 3 | Non-refundable credits & other payments |
| Schedule A | Itemized deductions (e.g., mortgage interest, medical expenses) |
| Schedule B/C/D/E/F/SE | Specific income sources like interest/dividends, business, capital, supplemental, farm, self-employed |
5. Key Stats & Trends
-
The IRS processes around 140 million individual returns, with a 1.5% increase in processed returns and refunds averaging $2,945 in 2025
-
Over 73 million e-filed returns were filed through professionals; roughly 64 million were self-prepared
-
Filing season stats show around 95% of returns filed by mid-season, representing 87% of Adjusted Gross Income and 82% of tax liability
6. Real-Life Examples
Example 1: Single Employee with Interest Income
-
Income: $50,000 salary + $500 bank interest
-
Standard deduction: $14,600
-
Taxable income: $35,900
-
Tax (using tables): ~$4,138
-
Withholding: $4,500 ⇒ Refund: ~$362
Example 2: Freelance Graphic Designer
-
Income: $30,000 freelance
-
Expenses: $5,000 business expenses (Schedule C)
-
Net income: $25,000
-
Self-employment tax: ~15.3% of $25,000 = $3,825
-
Standard deduction: $14,600
-
Taxable income: $10,400
-
Estimated tax excluding self-employment tax: ~$1,040
-
Total owed: $1,040 + $3,825 = $4,865
7. Practical Tips
-
Start early — avoid last-minute rush.
-
Use e-file & direct deposit — refunds typically arrive in 21 days
-
Double-check key entries — SSN, bank account numbers, withholding.
-
Track receipts for itemizing — big expenses like mortgage, charitable giving.
-
File Schedule C correctly — clearly track income vs. expenses.
-
Use available credits — e.g., Earned Income Credit, education.
-
Avoid underpayment penalties — estimate and pay quarterly if self-employed.
-
Review IRS stats — to benchmark your filing time, refund size .
8. Conclusion
Form 1040 may seem complex, but when broken into steps—income, deductions, taxes, payments—it becomes manageable. With the knowledge above, you're better prepared to file confidently, avoid mistakes, and maximize your refund. And remember, extra help is just a click away!
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: When is the deadline to file Form 1040?
Most years, it's April 15. Extensions may apply.
Q2: Should I itemize or take the standard deduction?
Itemize if your deductible expenses (mortgage, medical, charitable) exceed the standard deduction.
Q3: What if I underpay taxes?
You may owe penalties and interest. Consider quarterly estimated payments if self-employed.
Q4: Can I e-file Form 1040?
Yes—over 90% of filers e-file for faster processing .
Q5: How long will it take to get my refund?
Typically 21 days via e-file + direct deposit .
Q6: What records should I keep?
Keep W-2s, 1099s, receipts, bank statements, and E-file confirmation for 3–7 years.
10. Call to Action
👋 Need help filing your return?
At Manika Fintax Solutions, we offer paid filing support—friendly, affordable, and expert help to ensure accuracy and peace of mind. Contact us today to schedule a consultation!
Keywords: Form 1040, U.S. individual income tax, filing Form 1040, Schedule 1, Schedule C, tax refund, self-employment tax, filing tips, IRS statistics, tax credits.


Post a Comment
0Comments